Describe the Circulation of Deep Ocean Water
The combinations of salinity and cold temperatures make the water denser and cause it to sink to the bottom. The colder it got the denser the water would be and eventually that water would become dense enough to sink and become deep water.

Circulation Of The Seas National Geographic Society
As the surface layer moves away from the coast it is replaced by water that upwells from below the surface which brings colder water near the shore.
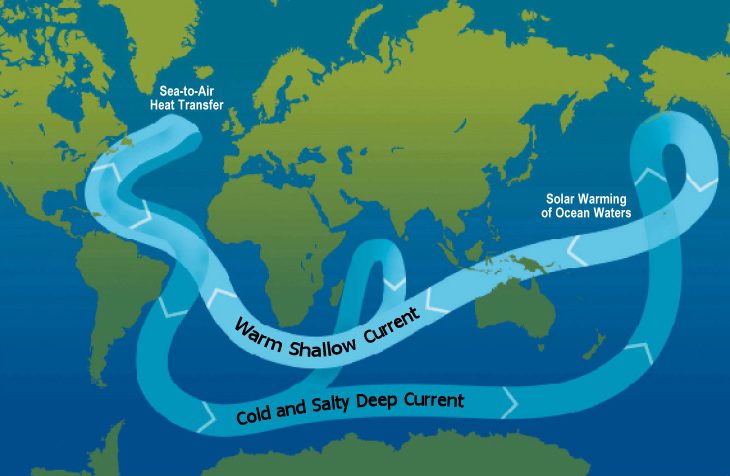
. 10 What causes deep ocean currents. Thermohaline circulation is a very slow and extremely deep movement of water in the oceans around the world. 1 the Gibraltar Strait 14 km wide and 300 m deep and the only connection between the Med Sea and the oceans and 2 the Sicily Channel 140 km wide and 500 m deep separating the Med Sea as two subbasins.
The conveyor belt also helps deliver oxygen to deep water habitats. The deep water began as cold surface water that was saturated with oxygen and when it sank it brought that oxygen to depth. These deep-ocean currents are driven by differences in the waters density which is controlled by temperature thermo and salinity haline.
Thermohaline circulation moves a massive current of water around the globe from northern oceans to. A combination of high salinity and low temperature near the. 8 Does water density increase with depth.
The earths crust is divided into 12 plate tectonics. Thermohaline circulation carries this oxygen-rich deep water throughout the oceans where the oxygen will be used by deep water organisms. Surface ocean currents include equatorial western boundary northern or.
Deep-water circulation brings dense cold oxygen-rich water from the surface to the deep ocean because of. I the fast wind-driven upper ocean circulation and ii the slow deep ocean circulation. 11 Where do density currents flow.
You just studied 9 terms. In contrast thermohaline circulation is much slower with a typical speed of 1 centimetre 04 inch per second but this flow extends to the seafloor and forms circulation patterns that envelop the. Deep Water Circulation.
7 How do density differences cause the large scale ocean circulation. These two components act simultaneously to drive the MOC the movement of seawater across basins and depths. The Gulf Stream carries salt into the high latitude North Atlantic where the water cools.
This process is known as thermohaline circulation. Oceanic circulation is driven by winds blowing over the ocean surface and. Now lets add in evaporation.
This circumpolar motion links the worlds oceans and allows the deep water circulation from the Atlantic to rise in the Indian and Pacific Oceans and the surface circulation to close with the northward flow in the Atlantic. The oceanic crust is up to 7km thick it is denser than the continental crust which is between 10 and 70km. From the wind direction in a process called Ekman transport.
6 What cause increase density that results in deep ocean current. The deep ocean is a huge storehouse of heat carbon oxygen and nutrients. Describe How Density Affects The Flow Of Deep CurrentsDense water sinks below less dense water.
Thermohaline circulation is another thing to think about when discussing deep ocean currents. A process known as thermohaline circulation or the ocean conveyor belt drives these deep underwater currents. 101 Concept Checks.
Ocean water is constantly moving. The Western Med Sea West Med and the East Med. It then flows southward deep along the ocean floor of the Atlantic Ocean through the Indian Ocean eventually mixing with the surface currents in the Pacific Ocean.
Global ocean circulation can be divided into two major components. As the name suggests the wind-driven circulation is. Thermohaline circulation is the process whereby surface seawater becomes denser at high latitudes and sinks to form new deep water.
Describe think annotated diagram the distribution of oceans and ocean currents including both surface currents and thermohaline deep water circulation. 9 How does density affect water circulation quizlet. The low overturning rate stabilizes our global climate.
It is also known as The Great Ocean Conveyor because it. Wind-driven circulation which is strongest in the surface layer of the ocean is the more vigorous of the two and is configured as large gyres that dominate an ocean region. This is the principle that drives the deep ocean currents that circulate around the world.
Deep waters are formed where the air temperatures are cold and where the salinity of the surface waters are relatively high. The North Pacific Ocean is known as the endpoint of the global thermohaline circulation which starts from the deep water formation in the northern North Atlantic Ocean and around Antarctica 123. 5 Are deep currents caused by density.
For example think about what would happen if a large scale surface current continually lost heat. Density differences in water masses. The Oceans Surface Circulat.
A complete cycle can take thousands of years to complete from start to finish with the cycle contributing a great deal to the mixing of the worlds oceans. As a result both the surface and deep waters flow from west to east around Antarctica. Deep-ocean is driven by changes in water density due to variations.
The Mediterranean thermohaline circulation is strongly affected by two key circulatory constrictions. This process is known as thermohaline circulation. The Coriolis effect impacts ocean currents by moving them at an angle away.
Now up your study game with Learn mode. Thermohaline circulation appears to be linked to global climate and ocean health. By carrying oxygen into the deeper layers it supports the largest habitat on earth.
Greater dissolution of oxygen in colder water than warmer water Briefly describe the different ways that ocean currents are measured. Ocean-atmosphere interactions have important implications for global ocean currents. Asked Nov 26 2020 in Environmental Atmospheric Sciences by CooperAtlas.
It takes around 1000 years for deep water to go around the oceans conveyor belt another name for deep-ocean circulation. Deep-ocean circulation occurs on a much longer time scales then surface currents. The surface current flows back throughout the Indian Ocean into the Atlantic Ocean returning surface water to the North Atlantic Ocean and driving the Gulf Stream The Gulf Stream flows along the east coast of the.
Deep ocean circulation regulates uptake distribution and release of these elements.
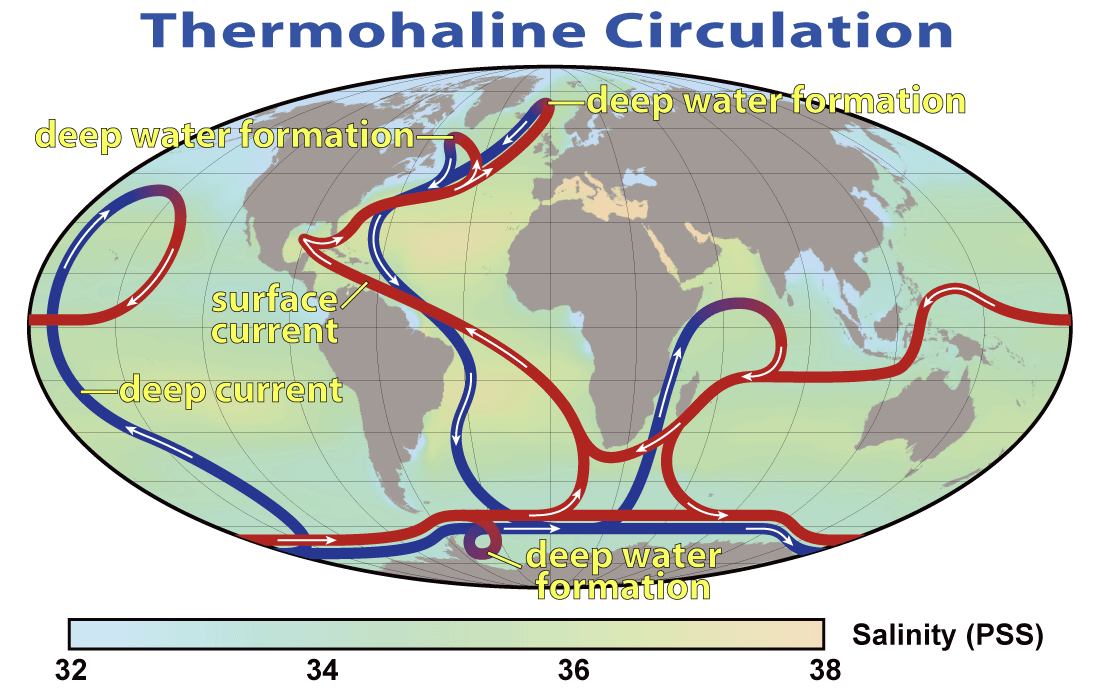
9 8 Thermohaline Circulation Introduction To Oceanography

0 Response to "Describe the Circulation of Deep Ocean Water"
Post a Comment